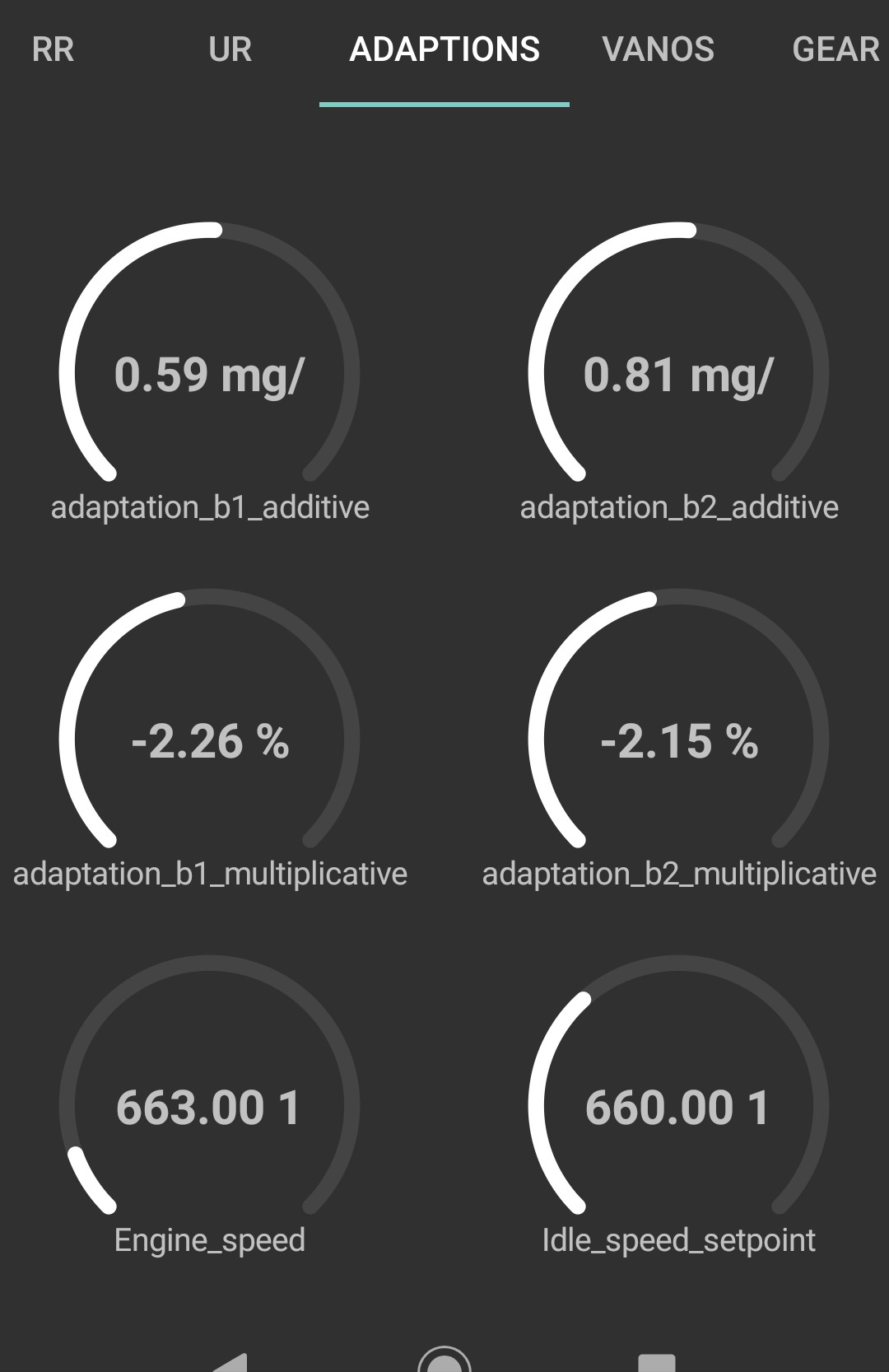
Mixture Adaptations of a N52b25 with an internal vacuum leak
The screenshot shows that the PCM -in both banks- is adding lots of fuel at idle and very low throttle but substracting it at higher RPM.
This is because the higher the engine RPM , the less impact an internal vacuum leak has on performance and fuel effeciency.
Bank 2 is the most impacted (0.81 mg per stroke). Theoritically the DME tries its best in keeping the engine balanced, which means in this case that Bank 2 is driving Bank 1